Approximate FP8
FP8 Format & Multiplication
FP8 is a natural progression from the FP16 representations, effectively reducing memory consumption and improving memory access and computational efficiency. Compared to traditional INT8, FP8 offers a larger dynamic range (the commonly used E4M3 format, as shown in Fig). Moreover, FP8 achieves less accuracy loss during NN inference. The FP8 format adheres to IEEE-754 conventions, where a real numbers is encoded by using a 1-bit sign S, an e-bit integer exponent E and an m-bit fractional (mantissa M),
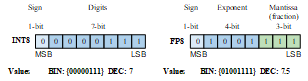
The demonstration of the INT8 and FP8 (E4M3)
The FP8 multiplication process of $x$ and $y$ can be represented as:
\[Mul(x,y) = M_x \cdot 2^{E_x} \times M_y \cdot 2^{E_y} \\ = (1+m_x) \cdot 2^{E_x} \times (1+m_y) \cdot 2^{E_y} \\ = (1+m_x+m_y+{\color{red}{m_x}} \cdot {\color{red}{m_y}})\cdot 2^{E_x+E_y}\]Only $m_x \cdot m_y$ involves a multiplication operation.
FPGA Structure
State-of-the-art FPGAs utilize basic logic cells such as multi-input LUTs, carry chains (adders), multiplexers, and D flip-flops to implement both combinational and sequential logic circuits.
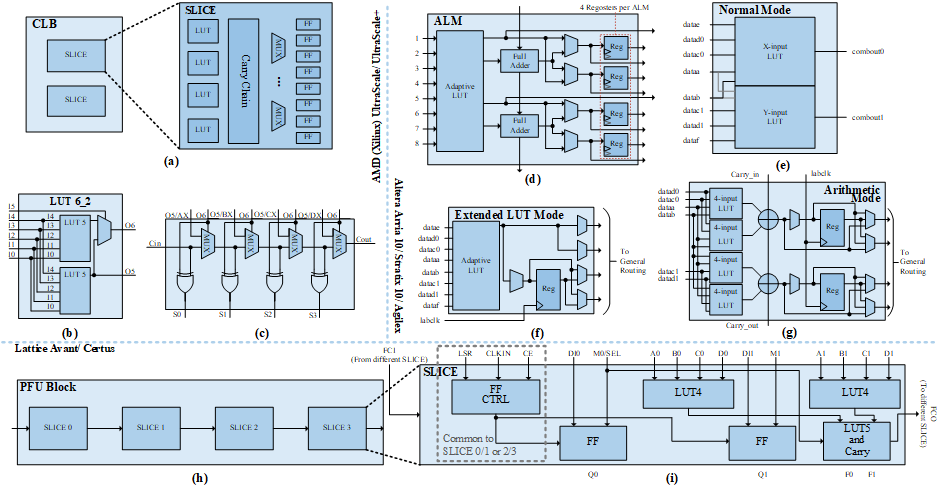
The state-of-the-art FPGA basic structure
Our efforts
Leveraging the L-Mul approximation, we developed LUT-based units and integrated them into FPGAs.
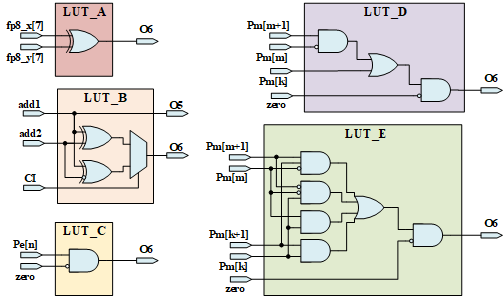
The five LUT-based basic components required for approximate multiplication.
To improve usability, we developed an automated generation tool. This tool features an intuitive graphical user interface (GUI) that allows users to customize settings based on their specific requirements, including the target device, choice between the two approximation methods, and FP8 data format. Once configured, FP8ApproxLib automatically generates the corresponding Verilog HDL code based on these parameters.
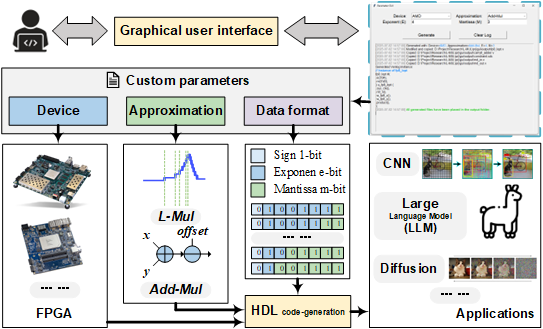
The overall generation flow and applications of FP8ApproxLib.
Publications
- FP8ApproxLib: An FPGA-Based Approximate Multiplier Library for
8-Bit Floating Point
JSA, 2026 - FPGA-Based Approximate Multiplier for FP8
FCCM, 2025